C# roguelike, devlog 11: Additional map generation algorithms
Introduction
In addition to the previously implemented noise, there are several algorithms that are quite useful to have at hand when working with procedural generation. A number of these, and some sample use cases are described in the fantastic Roguelike Celebration 2020 presentation Procedural Map Generation Techniques by Herbert Wolverson. Some of these algorithms, like BSP, Perlin noise and Dijkstra maps are already implemented in the project. In this post I’ll focus on adding algorithms for Cellular automata, Diffusion-limited aggregation (DLA), Drunkard’s Walk and 2D Voronoi diagrams.
Implementation
CellularAutomata.cs:
/// <summary>
/// Cellular automata (CA) algorithm.
/// </summary>
public static class CellularAutomata
{
// Run the algorithm and return a 2D map of booleans
public static bool[,] Run(ref uint seed, int width, int height, int iterations = 4, int percentOpen = 50)
{
bool[,] result = new bool[width, height];
// Setup random map
int randomColumn = Lfsr.MakeInt(ref seed, min: (uint)4, max: (uint)(width - 4));
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++)
{
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++)
{
// Random change to set open space (exclude map edges)
if(
!(x == 0 || y == 0 || x == width - 1 || y == height - 1)
&& (x == randomColumn || Lfsr.MakeInt(ref seed, min: (uint)1, max: (uint)100) < percentOpen)
)
result[x, y] = true;
}
}
// Run iterations
for(int i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
bool[,] iterationResult = new bool[width, height];
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++)
{
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++)
{
// Cellular automata logic (exclude map edges)
if(!(x == 0 || y == 0 || x == width - 1 || y == height - 1))
{
// Set rules
int adjacent = Adjacent(result, width, height, x, y);
iterationResult[x, y] = (adjacent < 5);
}
}
}
result = iterationResult;
}
// Return the complete map
return result;
}
// Count adjacent non-open spaces
private static int Adjacent(bool[,] result, int width, int height, int x, int y)
{
int adjacent = 0;
for (int newX = x - 1; newX <= x + 1; newX++)
{
for (int newY = y - 1; newY <= y + 1; newY++)
{
if (!result[newX, newY]) { adjacent++; }
}
}
return adjacent;
}
// Count nearby non-open spaces
private static int Nearby(bool[,] result, int width, int height, int x, int y, int distance = 2)
{
int nearby = 0;
for (int newX = x - distance; newX <= x + distance; newX++)
{
for (int newY = y - 2; newY <= y + 2; newY++)
{
if (Math.Abs(newX - x) == distance && Math.Abs(newY - y) == distance) { continue; }
if (newX < 0 || newY < 0 || newX >= width || newY >= height) { continue; }
if (!result[newX, newY]) { nearby++; }
}
}
return nearby;
}
}
DiffusionLimitedAggregation.cs:
/// <summary>
/// Diffusion-limited aggregation (DLA) algorithm.
/// </summary>
public static class DiffusionLimitedAggregation
{
// Run the algorithm and return a 2D map of booleans
public static bool[,] Run(ref uint seed, int width, int height, int percentOpen = 20, bool outwards = false)
{
bool[,] result = new bool[width, height];
// Check how many cells should be set to true for the generation to be considered finished
int remaining = (int)(((float)width * (float)height) * ((float)percentOpen * 0.01f));
// Set center area to true
result[(int)(width / 2) + 0, (int)(height / 2) + 0] = true;
result[(int)(width / 2) + 0, (int)(height / 2) + 1] = true;
result[(int)(width / 2) + 1, (int)(height / 2) + 0] = true;
result[(int)(width / 2) + 1, (int)(height / 2) + 1] = true;
// Start the loop
while (remaining > 0)
{
// Select a random starting point
Vec2 pos = new Vec2(outwards ? (int)(width / 2) : Lfsr.MakeInt(ref seed, min: (uint)0, max: (uint)width), outwards ? (int)(height / 2) : Lfsr.MakeInt(ref seed, min: (uint)0, max: (uint)height));
// Walk in a random direction until open space is found
while(true)
{
// Select a random direction to go next
Vec2 dest = pos + new Vec2(Lfsr.MakeInt(ref seed, min: (uint)0, max: (uint)2) - 1, Lfsr.MakeInt(ref seed, min: (uint)0, max: (uint)2) - 1);
// Abort and select a new direction if chosen direction is out of bounds
if (dest.x < 0 || dest.x >= width || dest.y < 0 || dest.y >= height) { break; }
// Check if open space is found
else if (outwards ? !result[dest.x, dest.y] : result[dest.x, dest.y])
{
if (outwards) { result[dest.x, dest.y] = true; }
else { result[pos.x, pos.y] = true; }
remaining--;
break;
}
// Change to new position
pos = dest;
}
}
return result;
}
}
DrunkardsWalk.cs:
/// <summary>
/// Drunkard's walk algorithm.
/// </summary>
public static class DrunkardsWalk
{
// Run the algorithm and return a 2D map of booleans
public static bool[,] Run(ref uint seed, int width, int height, int splits = 2, int percentOpen = 10)
{
bool[,] result = new bool[width, height];
// Place a drunkard on the map and walk around, setting walked locations to true
for (int i = 0; i < splits; i++)
{
// Check how many cells should be set to true for the walk to be considered finished
int remaining = (int)((((float)width * (float)height) * ((float)percentOpen * 0.01f)) / (float)splits);
// Select a random starting point
Vec2 pos = new Vec2(Lfsr.MakeInt(ref seed, min: (uint)0, max: (uint)width), Lfsr.MakeInt(ref seed, min: (uint)0, max: (uint)height));
// Walk until the desired number of cells has been set to true
while (remaining > 0)
{
// Select a random direction to go next
Vec2 dest = pos + new Vec2(Lfsr.MakeInt(ref seed, min: (uint)0, max: (uint)2) - 1, Lfsr.MakeInt(ref seed, min: (uint)0, max: (uint)2) - 1);
// Abort and select a new direction if chosen direction is out of bounds
if (dest.x < 0 || dest.x >= width || dest.y < 0 || dest.y >= height) { continue; }
// Check if open space is found
if (!result[dest.x, dest.y])
{
result[dest.x, dest.y] = true;
remaining--;
}
// Change to new position
pos = dest;
}
}
return result;
}
}
Voronoi.cs:
using System.Numerics;
/// <summary>
/// Voronoi diagram.
/// </summary>
public static class Voronoi
{
// Run the algorithm and return a 2D map of booleans
public static int[,] Run(ref uint lfsrSeed, int width, int height, int numSeeds = 10, bool manhattan = false)
{
int[,] result = new int[width, height];
// Create an array of unique Vec2 seeds
Vec2[] seeds = new Vec2[numSeeds];
for (int i = 0; i < numSeeds; i++)
{
while (seeds[i] == null)
{
// Select a random point
Vec2 point = new Vec2(Lfsr.MakeInt(ref lfsrSeed, min: (uint)0, max: (uint)(width - 1)), Lfsr.MakeInt(ref lfsrSeed, min: (uint)0, max: (uint)(height - 1)));
// Only add the point to the seeds if it doesn't exist already
bool pointExists = false;
foreach (Vec2 seed in seeds.Where(item => item != null))
{
if (seed.x == point.x && seed.y == point.y) { pointExists = true; break; }
}
if (!pointExists) { seeds[i] = point; }
}
}
// Check all cells in the map and find nearest seed
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++)
{
int nearest = 0;
float nearestDistance = 0f;
for (int i = 0; i < numSeeds; i++)
{
float distance = manhattan ? (float)Math.Abs(seeds[i].x - x) + (float)Math.Abs(seeds[i].y - y) : Vec2.Distance(new Vec2(x, y), seeds[i]);
if (i == 0 || distance < nearestDistance)
{
nearest = i;
nearestDistance = distance;
}
}
result[x, y] = nearest;
}
}
return result;
}
}
Conclusion
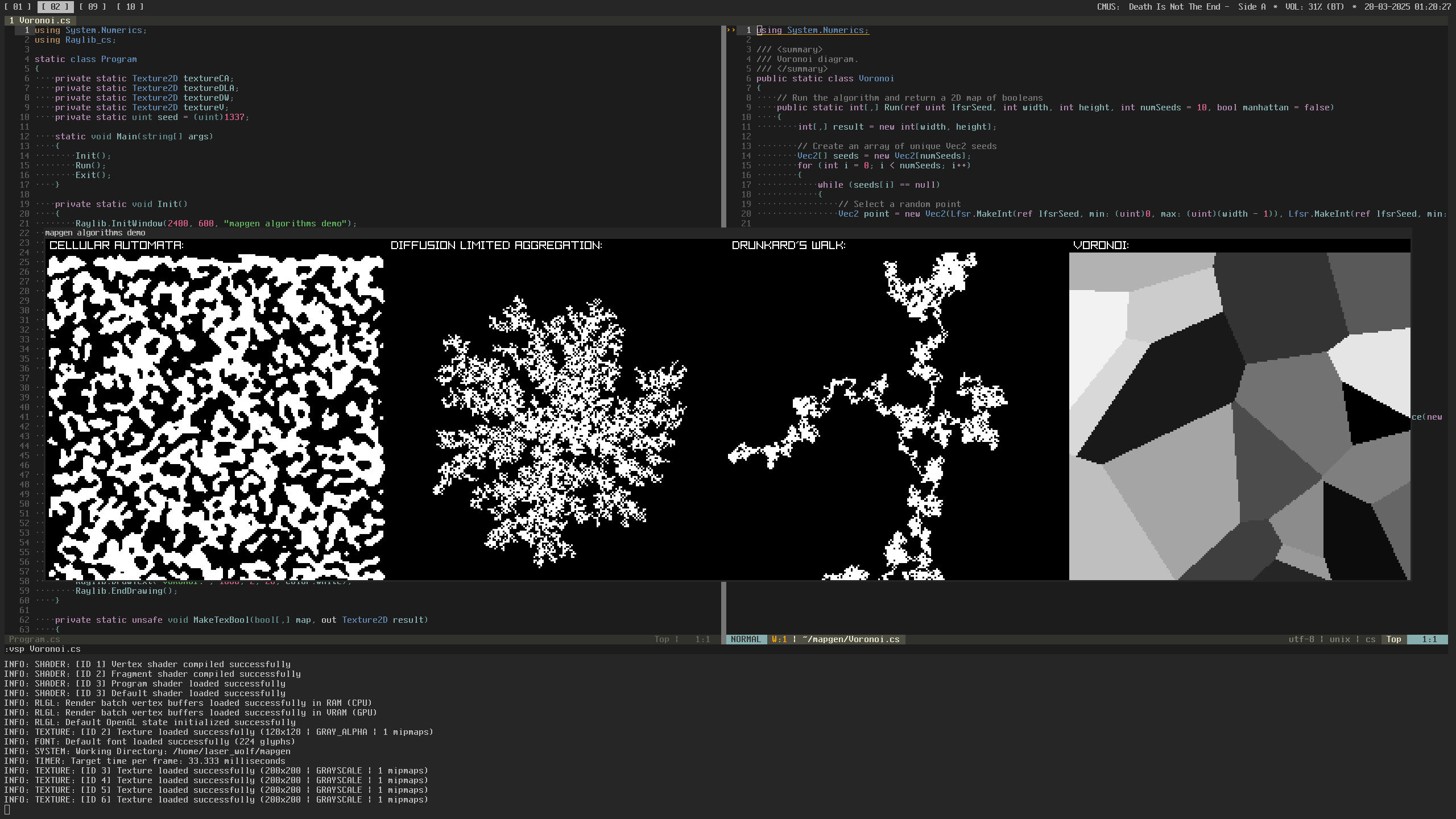
Here is a demo of the algorithms:
Download the demo source code: roguelike-devlog11_demo.zip
Find the project on GitHub: lzzrhx/roguelike