C# roguelike, devlog 10: Improved Perlin noise
Introduction
A more or less essential component needed for procedural generation is a good noise algorithm. In order to start working on terrain generation I’ll first add this to the project. I’ve opted for the Improved Perlin Noise algorithm. But another good alternative that is ready and available for C# is OpenSimplex2
This implementation is based on the following sources:
- Perlin, K. An image synthesizer
- Perlin, K. Improving noise
- Perlin, K. Implementing Improved Perlin Noise
- Perlin, K. Improved Noise reference implementation
- Perlin, K. Improved Noise reference implementation (4D)
- Biagioli, A. Understanding Perlin Noise
Implementation
This is a C# adaptation of the 4D Java reference implementation from Ken Perlin (linked in the list above) with methods for octaves added.
The Perlin class contains the following methods for generating noise:
Noise3()Generate 3D noise from a Vector2 position value and a float seed value.Noise4()Generate 4D noise from a Vector3 position value and a float seed value.Octave3()Generate octaved 3D noise from a Vector2 position value and a float seed value by calling theNoise3()multiple times and combining the result.Octave4()Generate octaved 4D noise from a Vector3 position value and a float seed value by calling theNoise4()multiple times and combining the result.
using System.Numerics;
/// <summary>
/// Improved Perlin Noise
/// </summary>
public static class Perlin {
//Fields
private static readonly int[] p = new int[512];
private static readonly int[] permutation = { 151,160,137,91,90,15,
131,13,201,95,96,53,194,233,7,225,140,36,103,30,69,142,8,99,37,240,21,10,23,
190, 6,148,247,120,234,75,0,26,197,62,94,252,219,203,117,35,11,32,57,177,33,
88,237,149,56,87,174,20,125,136,171,168, 68,175,74,165,71,134,139,48,27,166,
77,146,158,231,83,111,229,122,60,211,133,230,220,105,92,41,55,46,245,40,244,
102,143,54, 65,25,63,161, 1,216,80,73,209,76,132,187,208, 89,18,169,200,196,
135,130,116,188,159,86,164,100,109,198,173,186, 3,64,52,217,226,250,124,123,
5,202,38,147,118,126,255,82,85,212,207,206,59,227,47,16,58,17,182,189,28,42,
223,183,170,213,119,248,152, 2,44,154,163, 70,221,153,101,155,167, 43,172,9,
129,22,39,253, 19,98,108,110,79,113,224,232,178,185, 112,104,218,246,97,228,
251,34,242,193,238,210,144,12,191,179,162,241, 81,51,145,235,249,14,239,107,
49,192,214, 31,181,199,106,157,184, 84,204,176,115,121,50,45,127, 4,150,254,
138,236,205,93,222,114,67,29,24,72,243,141,128,195,78,66,215,61,156,180
};
// Constructor
static Perlin() { for(int i = 0; i < 512; i++) { p[i] = permutation[i % 256]; } }
// Linear interpolation between two floats
public static float Lerp(float x, float a, float b) { return a + x * (b - a); }
// Apply an ease curve to a float value by using the function 6t^5 - 15t^4 + 10t^3
public static float Fade(float t) { return t * t * t * (t * (t * 6f - 15f) + 10f); }
// Convert hash to 12 gradient directions
public static float Grad3(int hash, float x, float y, float z) {
// Mask lo 4 bits of hash code
// h = 1 1 1 1
// | | | |
// | | | bit 0
// | | bit 1
// | bit 2
// bit 3
int h = (hash & 15);
// u = x if hash bit 3 is 0
float u = h < 8 ? x : y;
// v = y if hash bit 2 and 3 are both 0
// else: v = x if hash bits are 1100 or 1110
// else: v = z
float v = h < 4 ? y : h == 12 || h == 14 ? x : z;
// Set u to negative if bit 0 is 1
// Set v to negative if bit 1 is 1
// Return u + v
return ((h & 1) == 0 ? u : -u) + ((h & 2) == 0 ? v : -v);
}
// Convert hash to 32 gradient directions
public static float Grad4(int hash, float x, float y, float z, float w) {
// Mask lo 5 bits of hash code
// h = 1 1 1 1 1
// | | | | |
// | | | | bit 0
// | | | bit 1
// | | bit 2
// | bit 3
// bit 4
int h = (hash & 31);
// Set default a, b, c to x, y, z
float a=y, b=z, c=w;
// Check bit 3 & 4
switch (h >> 3)
{
// Bit 3 is 1 and bit 4 is 0
case 1: a=w; b=x; c=y; break;
// Bit 3 is 0 and bit 4 is 1
case 2: a=z; b=w; c=x; break;
// Both bit 3 and 4 are 1
case 3: a=y; b=z; c=w; break;
}
// Set a to negative if bit 2 is 0
// Set b to negative if bit 1 is 0
// Set c to negative if bit 0 is 0
// Return a + b + c
return ((h & 4) == 0 ? -a : a) + ((h & 2) == 0 ? -b : b) + ((h & 1) == 0 ? -c : c);
}
// Generate 3D noise from a 2D position and seed value
public static float Noise3(Vector2 pos, float seed = 0f) {
// Find unit cube that contains point
int x = (int)MathF.Floor(pos.X) & 255;
int y = (int)MathF.Floor(pos.Y) & 255;
int z = (int)MathF.Floor(seed) & 255;
// Find relative position of point in cube
pos.X -= MathF.Floor(pos.X);
pos.Y -= MathF.Floor(pos.Y);
seed -= MathF.Floor(seed);
// Compute fade curves
float f = Fade(pos.X);
float g = Fade(pos.Y);
float h = Fade(seed);
// Hash coordinates of the cube corners
int a = p[x ] + y;
int b = p[x + 1] + y;
int aa = p[a ] + z;
int ab = p[a + 1] + z;
int ba = p[b ] + z;
int bb = p[b + 1] + z;
// Return blend result from all cube corners
return (Lerp(h, Lerp(g, Lerp(f, Grad3(p[aa ], pos.X , pos.Y , seed ),
Grad3(p[ba ], pos.X - 1f, pos.Y , seed )),
Lerp(f, Grad3(p[ab ], pos.X , pos.Y - 1f, seed ),
Grad3(p[bb ], pos.X - 1f, pos.Y - 1f, seed ))),
Lerp(g, Lerp(f, Grad3(p[aa + 1], pos.X , pos.Y , seed - 1f ),
Grad3(p[ba + 1], pos.X - 1f, pos.Y , seed - 1f )),
Lerp(f, Grad3(p[ab + 1], pos.X , pos.Y - 1f, seed - 1f ),
Grad3(p[bb + 1], pos.X - 1f, pos.Y - 1f, seed - 1f )))) + 1f) / 2f;
}
// Generate 4D noise from a 3D position and seed value
public static float Noise4(Vector3 pos, float seed = 0f) {
// Find unit hypercube that contains point
int x = (int)MathF.Floor(pos.X) & 255;
int y = (int)MathF.Floor(pos.Y) & 255;
int z = (int)MathF.Floor(pos.Z) & 255;
int w = (int)MathF.Floor(seed) & 255;
// Find relative position of point in hypercube
pos.X -= MathF.Floor(pos.X);
pos.Y -= MathF.Floor(pos.Y);
pos.Z -= MathF.Floor(pos.Z);
seed -= MathF.Floor(seed);
// Compute fade curves
float f = Fade(pos.X);
float g = Fade(pos.Y);
float h = Fade(pos.Z);
float i = Fade(seed);
// Hash coordinates of the hypercube corners
int a = p[x ] + y;
int b = p[x + 1] + y;
int aa = p[a ] + z;
int ab = p[a + 1] + z;
int ba = p[b ] + z;
int bb = p[b + 1] + z;
int aaa = p[aa ] + w;
int aab = p[aa + 1] + w;
int aba = p[ab ] + w;
int abb = p[ab + 1] + w;
int baa = p[ba ] + w;
int bab = p[ba + 1] + w;
int bba = p[bb ] + w;
int bbb = p[bb + 1] + w;
// Return blend result from all hypercube corners
return (Lerp(i, Lerp(h, Lerp(g, Lerp(f, Grad4(p[aaa ], pos.X , pos.Y , pos.Z , seed),
Grad4(p[baa ], pos.X - 1f, pos.Y , pos.Z , seed)),
Lerp(f, Grad4(p[aba ], pos.X , pos.Y - 1f, pos.Z , seed),
Grad4(p[bba ], pos.X - 1f, pos.Y - 1f, pos.Z , seed))),
Lerp(g, Lerp(f, Grad4(p[aab ], pos.X , pos.Y , pos.Z - 1f, seed),
Grad4(p[bab ], pos.X - 1f, pos.Y , pos.Z - 1f, seed)),
Lerp(f, Grad4(p[abb ], pos.X , pos.Y - 1f, pos.Z - 1f, seed),
Grad4(p[bbb ], pos.X - 1f, pos.Y - 1f, pos.Z - 1f, seed)))),
Lerp(h, Lerp(g, Lerp(f, Grad4(p[aaa + 1], pos.X , pos.Y , pos.Z , seed - 1f),
Grad4(p[baa + 1], pos.X - 1f, pos.Y , pos.Z , seed - 1f)),
Lerp(f, Grad4(p[aba + 1], pos.X , pos.Y - 1f, pos.Z , seed - 1f),
Grad4(p[bba + 1], pos.X - 1f, pos.Y - 1f, pos.Z , seed - 1f))),
Lerp(g, Lerp(f, Grad4(p[aab + 1], pos.X , pos.Y , pos.Z - 1f, seed - 1f),
Grad4(p[bab + 1], pos.X - 1f, pos.Y , pos.Z - 1f, seed - 1f)),
Lerp(f, Grad4(p[abb + 1], pos.X , pos.Y - 1f, pos.Z - 1f, seed - 1f),
Grad4(p[bbb + 1], pos.X - 1f, pos.Y - 1f, pos.Z - 1f, seed - 1f))))) + 1f) / 2f;
}
// Generate combined octaves of 3D noise
public static float Octave3(Vector2 pos, float seed = 0f, int octaves = 4, float persistence = 0.5f) {
float result = 0;
float frequency = 1;
float amplitude = 1;
float amount = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < octaves; i++)
{
result += Noise3(pos * frequency, seed) * amplitude;
amount += amplitude;
amplitude *= persistence;
frequency *= 2;
}
return result / amount;
}
// Generate combined octaves of 4D noise
public static float Octave4(Vector3 pos, float seed = 0f, int octaves = 4, float persistence = 0.5f) {
float result = 0;
float frequency = 1;
float amplitude = 1;
float amount = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < octaves; i++)
{
result += Noise4(pos * frequency, seed) * amplitude;
amount += amplitude;
amplitude *= persistence;
frequency *= 2;
}
return result / amount;
}
}
Conclusion
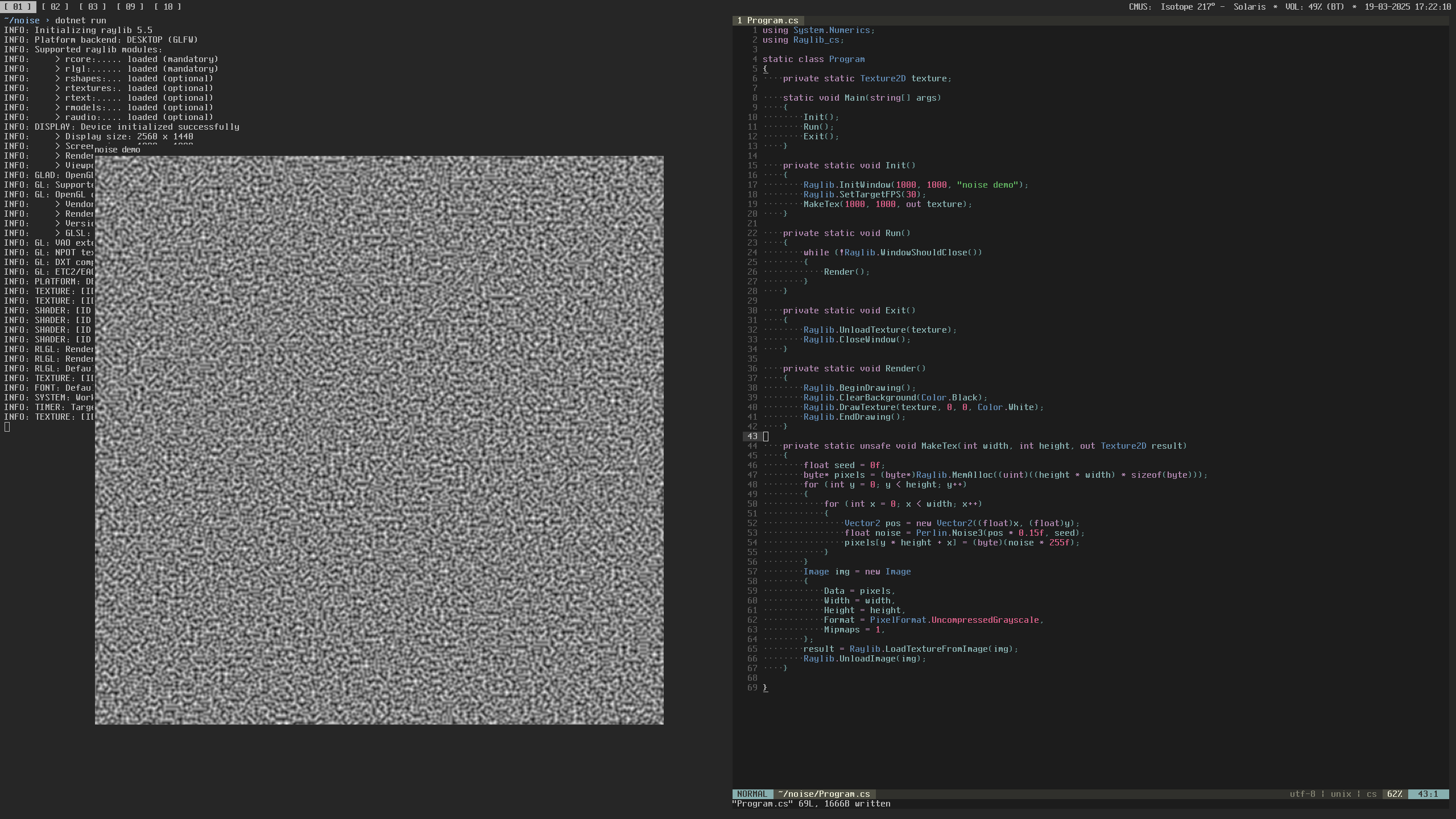
Here is a simple example of generating 3D noise (from a 2D position and a seed value set to 0):
Download the demo source code: roguelike-devlog10_demo.zip
Find the project on GitHub: lzzrhx/roguelike